The word “Plastic” was originally defined as “flexible and easily shaped”. The first plastic material was created in the mid-1800s. Then, the popularity of plastics grew around the world due to their innovative potential and unique properties. Plastic materials offer several advantages, including the ability to mass-produce them, as well as their lightweight, strength, durability, and low cost.
Plastics offer alternative solutions to society’s fast-changing needs. Today, plastics are used for many different purposes. Plastics, for example, enable society to have access to clean water, adequate sewage systems, safe food and hygienic healthcare.
According to PlasticsEurope, the European plastics industry ranks 7th in Europe in terms of industrial value-added contribution. Manufacturers of plastics machinery, raw materials, plastics converters, and plastics recyclers are all part of the European plastics sector. The European plastics industry employs around 1.56 million people and comprises 55,000 businesses. Most of them are small and medium-sized enterprises. In 2019, almost 58 million tonnes of plastics were produced throughout Europe (EU28). The European demand for plastics was 50.7 million tonnes. The European turnover of the plastics industry was more than 350 billion euros. The plastics sector provided 28.5 billion euros to European public finances and welfare.
Plastics were initially created as a means of preserving the availability of natural resources, such as wood, metals or ivory; however, mismanaged plastic waste is now a major threat to our ecosystem.
The major part of plastic waste is generated in the post-consumer market, including industrial and agricultural plastic waste and plastics collected from residential and business customers. Usually pre-consumer plastic waste is directly disposed of and recycled in the plastic factories.
Plastic is a material that can be recycled and reused practically indefinitely. We need to rethink our relationship with the materials we use: how we produce them, dispose of them, and how we can recycle them to avoid the consumption of virgin materials. – Silvia Merighi, director of the MSP Group, Broker in the recycled plastic industry.
According to PlasticsEurope, 29.1 million tonnes of plastic post-consumer waste were collected to be treated throughout Europe. Graph 1 shows waste treatment distribution in Europe between 2006 and 2018.
Since 2006 the amount of plastic waste collected has increased by 19%.
Despite the fact that the amount of waste disposed of in landfills has fallen considerably (by 44%), it still accounted for 24.9 percent of total waste collected in Europe in 2018. The amount of plastic waste sent to recycling has doubled from 2006 to 2018. The amount of plastic waste treated with energy recovery increased by 77%. In 2018 recycling and incineration of plastic waste in Europe reached respectively 32.5% and 42.6%.
Graph1 – Plastic post-consumer waste treatment in Europe, in million tonnes.
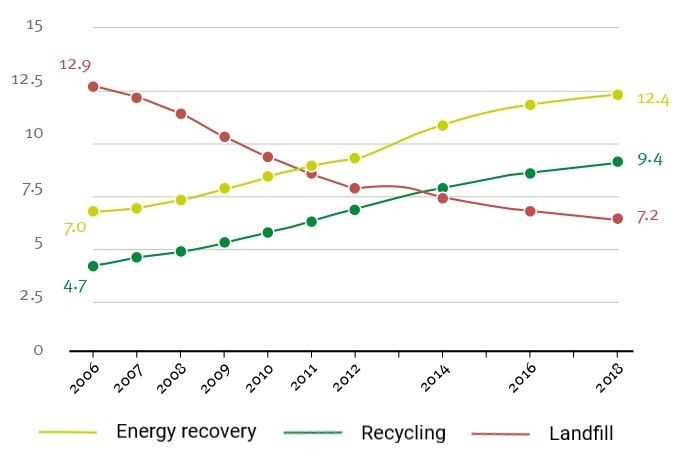
Source: PlasticsEurope, 2020.